Welcome to the Astronomy Vocabulary Page! This page is dedicated to providing you with a comprehensive list of astronomy-related terms. You can expect to find links to games, flashcards, and other resources to help you study and master the vocabulary associated with this subject. Dive in and expand your knowledge of the stars and beyond!
Astronomy is the scientific study of celestial objects, such as stars, planets, comets, and galaxies, as well as phenomena that originate outside the Earth’s atmosphere. Astronomers use telescopes and other instruments to observe and analyze these objects and their movements. This field of science has led to groundbreaking discoveries about the origins of the universe, the nature of black holes, and the potential for life on other planets. Studying astronomy can deepen our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it.
Practice & Reinforce Your Learning
Astronomy Vocabulary List
Stars

- The telescope allowed us to observe the celestial bodies in great detail.
- The ancient Greeks believed that the celestial bodies were controlled by gods.
- Astronomers use powerful telescopes to study the movement of celestial objects.

- The constellation Orion is easily recognizable in the winter sky.
- My favorite constellation is Cassiopeia because it looks like a big W.
- The constellation Ursa Major, also known as the Big Dipper, is a popular sight in the northern hemisphere.

- The luminosity of the sun is approximately 3.8 x 10^26 watts.
- Astronomers use luminosity to understand the brightness and energy output of different celestial bodies.
- The luminosity of a star can be used to determine its size, temperature, and distance from Earth.

- The magnitude of the star was measured to be 3.5, indicating it was relatively bright in the night sky.
- Astronomers use a scale to compare the magnitudes of different stars, with negative numbers representing the brightest stars.
- The magnitude of a star can change over time as it evolves and experiences different stages of its lifecycle.
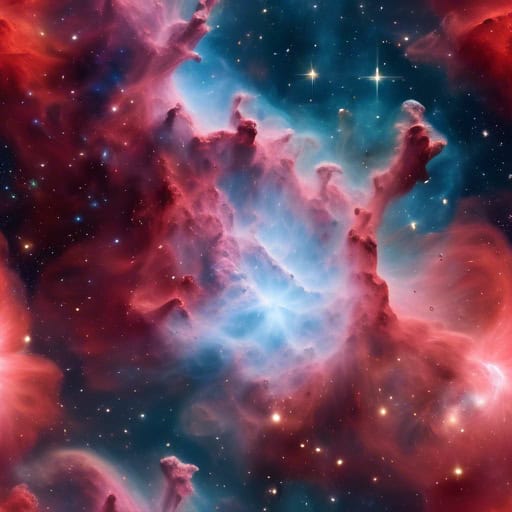

- The Hubble Space Telescope captured a stunning image of a colorful nebula in the Orion constellation.
- Scientists believe that the Crab Nebula was formed from a supernova explosion over a thousand years ago.
- Astronomers are constantly studying different types of nebulae to better understand the formation and evolution of stars.

- The astronomer's research on stellar formations was groundbreaking.
- Her performance in the play was absolutely stellar.
- The telescope's resolution was so stellar that it captured never-before-seen details of the galaxy.
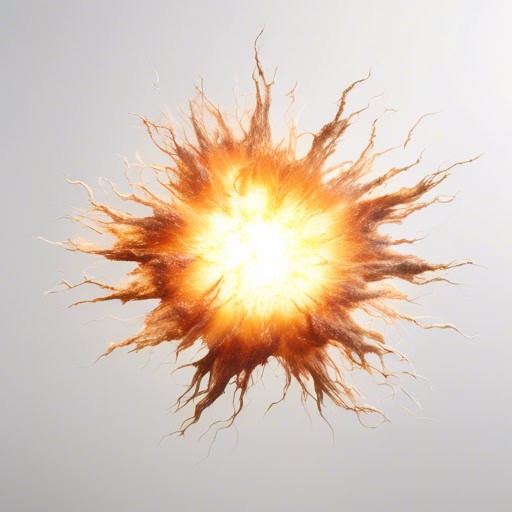

- The supernova was so bright that it outshone an entire galaxy, visible from light years away.
- Scientists observed the remnants of a supernova, studying the elements and energy released during the explosion.
- A supernova can release as much energy in a few days as the sun will in its entire lifespan.

- The Big Dipper is a well-known asterism within the constellation Ursa Major.
- The Summer Triangle is another famous asterism made up of the stars Deneb, Altair, and Vega.
- The Teapot asterism is found within the constellation Sagittarius and resembles its namesake.
Planets
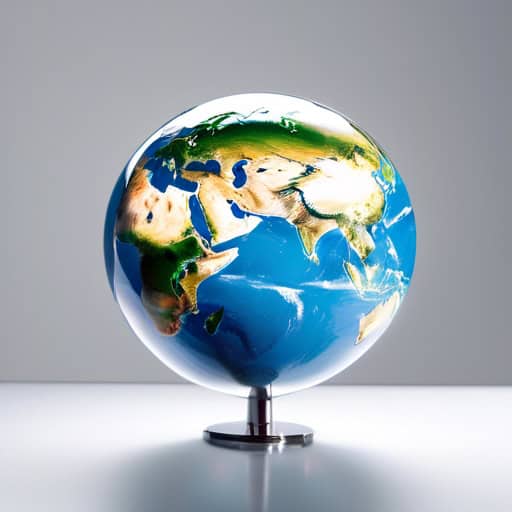

- The Earth is the only known planet in our solar system that supports life.
- Many scientists believe that Earth is the most hospitable planet for human life.
- Exploring the vast oceans and diverse landscapes of Earth is a thrilling adventure.
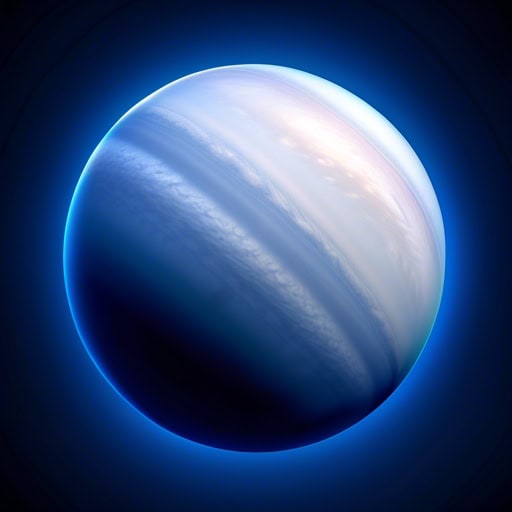

- Neptune's blue hue is due to the presence of methane in its atmosphere.
- The orbit of Neptune is highly elliptical, taking it to the outer reaches of our solar system.
- Neptune has a total of 14 known moons, with Triton being the largest and most well-known.
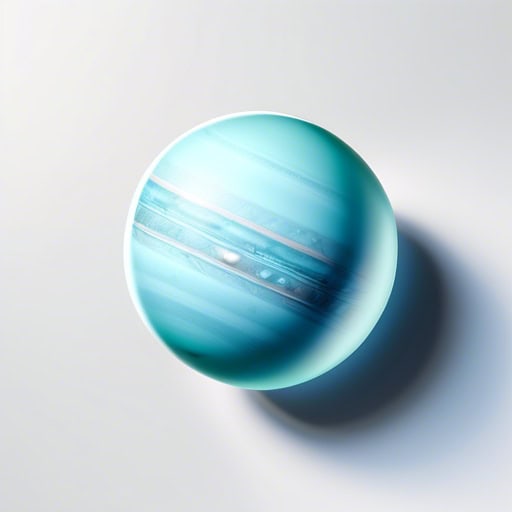

- Uranus is the only planet in our solar system that rotates on its side.
- Some scientists believe Uranus was knocked off its original axis by a massive collision.
- The unique tilt of Uranus causes extreme seasonal changes on the planet.
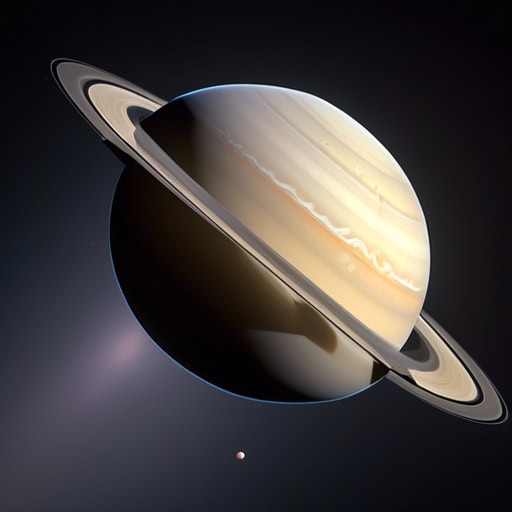

- Saturn is easily recognizable in the night sky due to its distinct rings shining brightly.
- Many astronomers are fascinated by the unique composition and structure of Saturn's rings.
- Saturn's rings are made up of countless particles ranging in size from tiny grains to massive chunks of ice and rock.
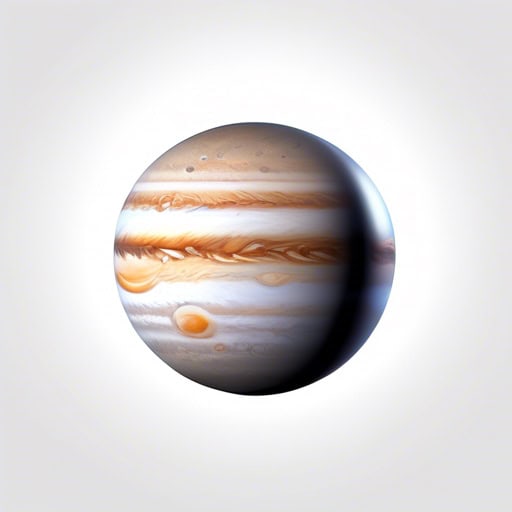

- Jupiter is the largest planet in our Solar System, with a diameter of over 86,000 miles.
- The Great Red Spot on Jupiter is a massive storm that has been raging for over 350 years.
- Jupiter has a total of 79 moons, with the four largest known as the Galilean moons.
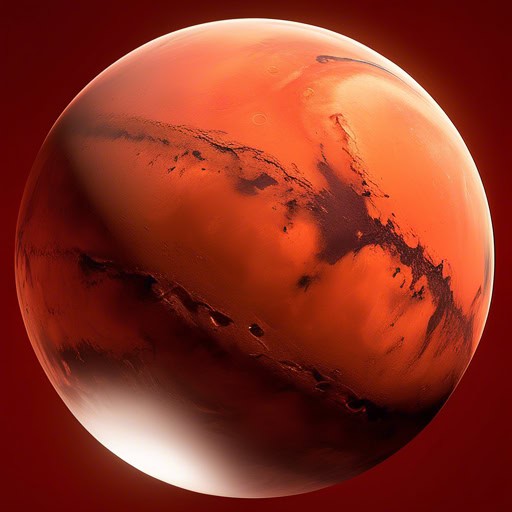

- Scientists have been studying Mars for decades in hopes of finding signs of past or present life.
- The Mars rover successfully landed on the planet's surface, sending back valuable data and images.
- Many believe that one day humans will be able to travel to Mars and potentially colonize it.

- Venus is often referred to as Earth's "sister planet" due to its similar size and composition.
- Many spacecraft have been sent to study Venus, including the Soviet Venera probes and NASA's Magellan mission.
- The surface of Venus is dominated by volcanic features, such as vast plains of hardened lava and numerous large volcanoes.

- Mercury's surface can reach scorching temperatures of up to 800 degrees Fahrenheit during the day.
- Despite its small size, Mercury has a surprisingly large iron core.
- Scientists believe that Mercury's surface may have been shaped by volcanic activity in the past.
Moons
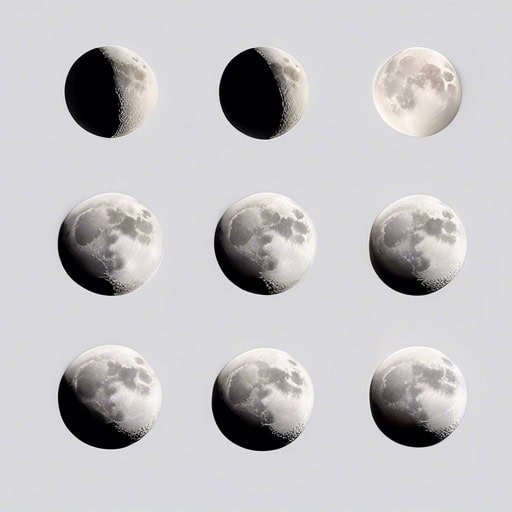

- During different phases of the Moon, we can observe its changing appearance in the night sky.
- The phases of the Moon are a result of its orbit around the Earth and the way sunlight reflects off its surface.
- Each month, the Moon transitions through its various phases, from new moon to full moon and back again.

- The surface of the moon is covered in craters and volcanic plains.
- Scientists are studying the surface of Mars to understand its geological history.
- Astronauts walking on the surface of a distant moon would need to wear protective suits.

- The crater on the moon was so large that it could be seen from Earth with a telescope.
- Astronauts explored the crater to collect samples of the moon's surface.
- Scientists believe that the crater was formed billions of years ago from a massive collision.

- The moon completes one full orbit around the Earth approximately every 27 days.
- Satellites are placed into specific orbits around the Earth to facilitate communication and data transmission.
- The International Space Station orbits the Earth at an average altitude of 420 kilometers.

- Earth's moon is the most well-known natural satellite in our solar system.
- Jupiter has over 79 natural satellites, the largest being Ganymede.
- The planet Saturn is known for its beautiful natural satellites, such as Titan and Enceladus.

- The satellite was launched into orbit to study the Earth's atmosphere.
- The communication satellite transmitted signals across the globe.
- Scientists used a powerful telescope to observe the movements of the distant satellite.

- The full moon shone brightly in the night sky.
- She gazed up at the crescent moon, feeling its mystical energy.
- The astronaut marveled at the beauty of Earth's moon from space.

- The lunar module successfully landed on the moon's surface.
- Scientists observed a lunar eclipse from their observatory.
- Jupiter's many moons include several that are considered lunar.
Constellations

- The Big Dipper is a popular constellation in the Northern Hemisphere.
- When I look up at the night sky, I love trying to find different constellations.
- The constellation Orion is known for its distinctive belt of three stars.

- The star in the night sky twinkled brightly, illuminating the darkness.
- She dreamed of becoming a famous movie star one day.
- The astronomer used a powerful telescope to study the distant star system.

- I am fascinated by the field of astronomy and love stargazing on clear nights.
- Studying astronomy has opened my eyes to the vastness and complexity of the universe.
- The study of astronomy has led to many important discoveries about the cosmos and our place in it.

- The astronomer used a powerful telescope to observe the celestial bodies in the night sky.
- Many ancient civilizations believed that the movement of celestial bodies influenced events on Earth.
- The planetarium offered a captivating show about the wonders of the celestial realm.

- The Milky Way is just one of billions of galaxies in the universe.
- Scientists study distant galaxies to learn more about the origins of the universe.
- The Andromeda galaxy is expected to collide with our own galaxy, the Milky Way, in about 4 billion years.

- My zodiac sign is Leo, which means I was born between July 23 and August 22.
- I enjoy reading my horoscope to see what the zodiac has in store for me each day.
- Many people believe that the zodiac can provide insight into their personalities and relationships.

- The study of the cosmos has led to groundbreaking discoveries about the origins and evolution of the universe.
- Many scientists believe that there may be other forms of life existing somewhere in the vast cosmos.
- Stargazing allows us to marvel at the beauty and complexity of the cosmos, inspiring a sense of wonder and curiosity.

- I used my telescope to observe the craters on the surface of the moon.
- The astronomers at the observatory use a powerful telescope to study black holes.
- She peered through the lens of the telescope and marveled at the rings of Saturn.
Dwarf planets

- Eris was discovered in 2005 and is known to be slightly larger than Pluto.
- The highly elliptical orbit of Eris takes it far from the sun at times, making it one of the most distant objects in our solar system.
- Scientists continue to study Eris to learn more about the outer reaches of our solar system.

- The Kuiper Belt is home to numerous icy bodies and asteroids.
- Scientists believe that the Kuiper Belt may contain billions of comets.
- The Kuiper Belt is named after Dutch-American astronomer Gerard Kuiper.

- Scientists have discovered numerous Trans-Neptunian objects in recent years, shedding light on the outer reaches of our solar system.
- Pluto is perhaps the most well-known Trans-Neptunian object, having been reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006.
- Eris, another Trans-Neptunian object, is slightly smaller than Pluto but has a highly eccentric orbit that takes it far from the Sun.

- Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006 by the International Astronomical Union.
- Ceres, the largest object in the asteroid belt, is considered a dwarf planet.
- There are currently five recognized dwarf planets in our solar system.

- Ceres was first discovered in 1801 and is named after the Roman goddess of agriculture.
- Scientists believe that Ceres may have a subsurface ocean beneath its icy crust.
- The Dawn spacecraft conducted a detailed study of Ceres, revealing its unique surface features and composition.

- Makemake is one of the largest known objects in the Kuiper Belt.
- The discovery of Makemake expanded our understanding of the outer solar system.
- The naming of Makemake after a Polynesian god reflects the cultural diversity in astronomy.

- Haumea is one of the five recognized dwarf planets in our solar system.
- Its elongated shape is believed to be the result of a collision with another celestial body.
- The rapid rotation period of Haumea contributes to its unique appearance and characteristics.

- Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006, causing controversy among astronomers.
- Some scientists believe that there may be more dwarf planets like Pluto waiting to be discovered in the Kuiper Belt.
- Pluto has a highly elliptical orbit that takes it closer to the sun than Neptune for part of its orbit.
Comets

- The comet streaked across the night sky, leaving a trail of dust and glowing debris in its wake.
- Scientists study comets to learn more about the early solar system and the origins of life on Earth.
- Many cultures throughout history have viewed comets as omens or signs of important events to come.

- The nucleus is the control center of the cell, housing the genetic material.
- The scientist studied the structure of the nucleus to better understand how it functions.
- The nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons.
- The comet tail stretched across the night sky, shimmering with a faint green hue.
- As the comet passed by, its tail left a trail of stardust in its wake.
- Astronomers eagerly studied the comet tail, hoping to unlock the mysteries of the cosmos.

- After the accident, the victim fell into a deep coma.
- The doctor explained that the patient's coma was due to severe head trauma.
- She spent weeks by her husband's bedside, praying for him to wake up from his coma.
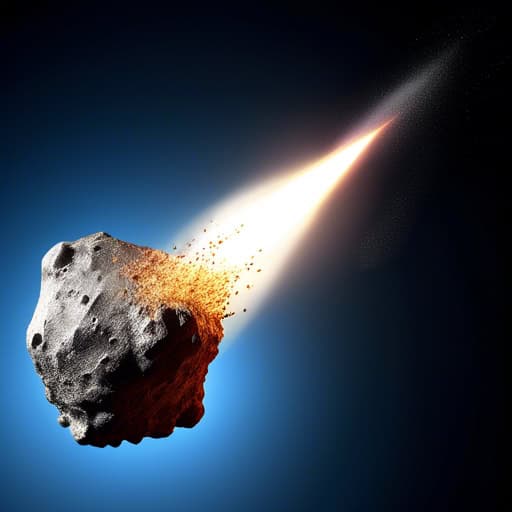

- A meteoroid entered Earth's atmosphere and produced a bright streak of light known as a meteor.
- Scientists study meteoroids to better understand the composition of objects in our solar system.
- Some meteoroids can survive the journey through Earth's atmosphere and reach the surface as meteorites.
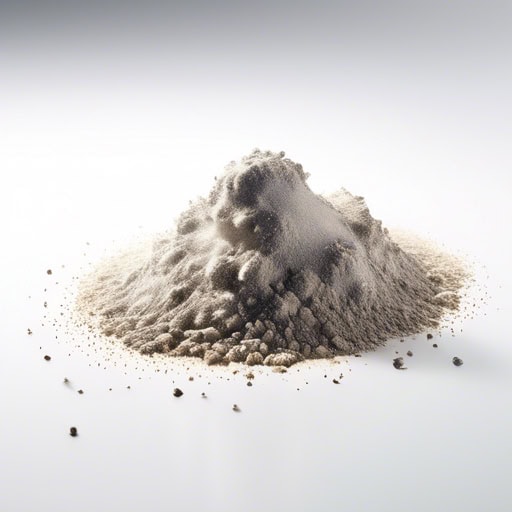

- Comet dust can provide valuable information about the composition of comets and the early solar system.
- Scientists study comet dust to learn more about the formation and evolution of our solar system.
- The collection of comet dust by spacecraft missions has yielded important insights into the origins of our celestial neighborhood.
Quick Facts
- One interesting fact about astronomy is that the universe is constantly expanding. This means that galaxies are moving away from each other at incredible speeds.
- Another fascinating fact is that the sun is actually a star, but it is the closest one to Earth. It provides heat and light to our planet, making life possible.
- Astronomers have discovered that there are more stars in the universe than grains of sand on all the beaches on Earth. This shows just how vast and endless space truly is.
- Black holes are another intriguing aspect of astronomy. These are regions in space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from them.
- Finally, astronomers have found evidence of water on Mars, leading to speculation about the possibility of life on the red planet. Studying other planets in our solar system is a key part of understanding our own place in the universe.
