On this page, you can expect to find a comprehensive botany vocabulary list along with links to games, flashcards, and other resources to help you master the subject. Explore the various terms and concepts related to botany engagingly and interactively. Get ready to expand your knowledge and deepen your understanding of this fascinating field of study.
Botany is the scientific study of plants, including their structure, growth, reproduction, metabolism, and classification. This field of biology plays a crucial role in understanding the diversity and importance of plant life on Earth. Botanists study how plants adapt to their environments, the ecological relationships between plants and other organisms, and how plants can be utilized for medicinal, agricultural, and environmental purposes. By exploring the intricate world of plants, botanists contribute to our knowledge of the natural world and help us better appreciate the beauty and complexity of plant life.
Practice & Reinforce Your Learning
Botany Vocabulary List
Plant Anatomy

- The root of the tree stretched deep into the soil, providing stability during strong winds.
- She pulled out the stubborn weed by its root, making sure to remove it entirely.
- His passion for music had its root in childhood memories of listening to his grandmother's piano playing.

- The fall breeze gently carried the colorful leaf off the tree and onto the ground.
- She pressed a delicate leaf between the pages of her journal as a keepsake from their nature walk.
- The leafy branches rustled in the wind, creating a soothing sound as they swayed back and forth.

- The node on the plant stem is where new growth typically occurs.
- The nodes of the plant provide support and facilitate the exchange of nutrients.
- Each node on the stem contains a bud that can develop into a new shoot or branch.

- The internode length can vary depending on the plant species.
- New branches typically form at each internode along the stem.
- The internode spacing can influence the overall growth pattern of the plant.
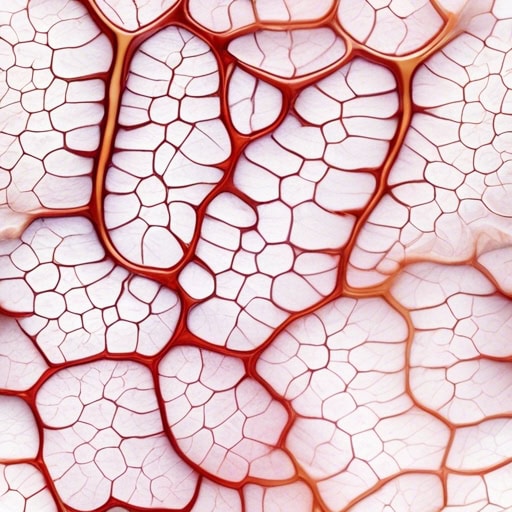
- The epidermis of the plant acts as a shield, preventing harmful substances from entering the plant's tissues.
- The epidermis also contains specialized cells called stomata, which regulate gas exchange and transpiration.
- Damage to the epidermis can leave the plant vulnerable to infections and dehydration.

- The xylem tissue in the plant's stems helps to transport water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves.
- Xylem cells are known for their ability to provide structural support to the plant.
- The efficiency of xylem in transporting water allows plants to survive and thrive in various environments.

- The phloem is responsible for transporting sugars produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Phloem is a crucial component of the plant's vascular system, working in conjunction with xylem to ensure proper nutrient distribution.
- When the phloem becomes damaged, it can disrupt the flow of nutrients throughout the plant, leading to stunted growth and poor health.

- The stem of the rose plant was green and sturdy, holding up the delicate blooms.
- I carefully cut the stem of the sunflower to place it in a vase of water.
- The thick stem of the oak tree provided a strong foundation for its sprawling branches.
Plant Physiology

- Plants require efficient nutrient uptake to ensure healthy growth and development.
- Nutrient uptake can be affected by factors such as soil pH, temperature, and root structure.
- Understanding the mechanisms of nutrient uptake in plants is crucial for optimizing crop production and plant health.

- Translocation is essential for the distribution of sugars and other organic compounds throughout the plant.
- The process of translocation helps ensure that all parts of the plant receive the necessary nutrients for growth and development.
- In plant physiology, translocation plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and functioning of the plant.

- During photosynthesis, plants undergo respiration to convert sunlight into energy.
- Proper respiration is vital for the survival of all living organisms.
- In plant physiology, respiration plays a crucial role in the overall growth and development of plants.

- The chlorophyll in plants is responsible for their green color.
- Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis to occur in plants.
- During photosynthesis, chlorophyll captures sunlight to produce energy for the plant.

- Stomata play a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis by allowing carbon dioxide to enter the leaf and oxygen to exit.
- During hot and dry conditions, plants can close their stomata to prevent excessive water loss through transpiration.
- The number and distribution of stomata on a leaf can vary depending on the plant species and environmental factors.

- Transpiration is an essential process for plants to regulate their temperature and transport nutrients.
- High temperatures can increase the rate of transpiration in plants, leading to water loss.
- Plants in arid environments have adapted to minimize transpiration to conserve water.

- During photosynthesis, plants use sunlight to produce their own food.
- Photosynthesis is a crucial process for the survival of plants and ultimately all living things.
- The oxygen released through photosynthesis is essential for the respiration of animals and humans.
Plant Taxonomy

- The taxonomy of roses involves categorizing them into various species, subspecies, and varieties.
- In biology, taxonomy is essential for organizing and understanding the vast diversity of living organisms.
- Modern advancements in molecular taxonomy have revolutionized the way scientists classify and study organisms.

- I am studying botany in college because I find plants fascinating.
- Botany involves identifying and classifying different plant species.
- The botany professor taught us about plant anatomy and how it affects their growth.

- The scientist discovered a new species of butterfly in the rainforest.
- There are over 300,000 known species of plants in the world.
- The endangered species of sea turtles are protected by conservation efforts.

- There are multiple species within the genus Rosa that are commonly known as roses.
- The genus Canis includes species such as wolves, dogs, and coyotes.
- In the plant kingdom, the genus Solanum contains species like tomatoes, potatoes, and eggplants.

- The rose family includes roses, apples, and cherries.
- Many members of the mint family have square stems and aromatic leaves.
- The legume family consists of plants like peas, beans, and peanuts.

- The classification of plants helps botanists and researchers identify and study different species.
- In plant taxonomy, classification plays a crucial role in understanding the diversity of plant life.
- The classification of plants is constantly evolving as new research provides more insights into their relationships and characteristics.

- The field of phylogenetics is constantly evolving as new genetic data becomes available.
- Researchers use phylogenetics to trace the evolutionary history of various species and understand their genetic relationships.
- Phylogenetics plays a crucial role in reconstructing the tree of life and uncovering the patterns of evolution across different organisms.
Plant Ecology

- The wetland ecosystem is home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, each playing a unique role in the balance of the environment.
- Human activities have greatly impacted the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem, leading to widespread pollution and habitat destruction.
- Protecting the fragile ecosystem of the rainforest is crucial for preserving biodiversity and ensuring the well-being of countless species.

- The cactus's ability to retain water is an adaptation that allows it to survive in arid environments.
- Some plants have developed deep root systems as an adaptation to access water in dry soil conditions.
- Leaf shape and coloration are examples of adaptations that help plants absorb sunlight for photosynthesis.

- There is fierce competition among plants in the forest for access to sunlight in order to photosynthesize effectively.
- The competition for water can be intense in arid regions where plants must compete for limited resources to survive.
- Plants in a dense forest ecosystem must constantly compete for nutrients in the soil to grow and thrive.

- Photosynthesis is a crucial process for the survival of plants, as it provides them with the energy they need to grow and thrive.
- Without photosynthesis, we would not have oxygen in the atmosphere, as it is the primary way in which oxygen is produced on Earth.
- Plants rely on photosynthesis to convert sunlight into usable energy, making it a fundamental process in the ecosystem.

- The rainforest is an important hotspot of biodiversity, containing a vast array of plant and animal species.
- Conservation efforts aim to protect and preserve biodiversity in order to maintain ecosystems and prevent species extinction.
- Climate change poses a threat to global biodiversity as habitats and ecosystems are disrupted and species struggle to adapt.

- The destruction of the rainforest is causing many animal species to lose their natural habitat.
- The preservation of wetlands is crucial for maintaining the habitat of many waterfowl species.
- Conservation efforts are being made to protect the habitat of endangered sea turtles.

- The plant community in this forest consists of oak, pine, and maple trees.
- The diversity of plant species within the wetland plant community provides habitat for various wildlife.
- Researchers are studying how climate change is affecting the composition of the plant community in the desert ecosystem.

- The tropical rainforest has a high species richness, with hundreds of different plant species coexisting.
- Conservation efforts aim to protect areas with high species richness to preserve biodiversity.
- Researchers are studying how climate change impacts species richness in coral reefs.
Plant Genetics

- The phenotype of the rose plant included red petals and thorns, which were inherited from its parent plants.
- The differences in leaf shape and flower color among the daisies were due to variations in their phenotypes.
- Through selective breeding, farmers were able to manipulate the phenotype of the corn plants to enhance their resistance to pests.

- The genotype of the strawberry plant determines its resistance to diseases.
- Selective breeding aims to improve the genotype of crops for higher yields.
- Understanding the genotype of a plant can help predict its characteristics and performance in different environments.

- Genetic modification has been a controversial topic in the agricultural industry for years.
- Scientists are constantly researching new ways to use genetic modification to improve crop yields.
- The process of genetic modification involves inserting or deleting specific genes in a plant's DNA.

- Gene expression can be influenced by various environmental factors in plants, such as light and temperature.
- Researchers are studying the regulation of gene expression in plant genetics to better understand how traits are inherited and passed on.
- Mutations in certain genes can disrupt the normal process of gene expression, leading to abnormal protein production in plants.

- Genetic engineering has revolutionized plant breeding by allowing scientists to create crops with increased pest resistance.
- Farmers are increasingly relying on genetic engineering to increase crop yields and improve the nutritional content of their plants.
- Opponents of genetic engineering argue that it poses risks to the environment and human health.

- Genetic variation plays a crucial role in plant breeding programs by allowing for the selection of traits that can improve crop yield and resilience to environmental stressors.
- Studying genetic variation in plants can help scientists understand the underlying mechanisms that drive evolution and adaptation in different species.
- Genetic variation is essential for the long-term survival of plant populations, as it provides the necessary diversity for plants to adapt to changing environmental conditions.

- The plant genome contains all the genetic information necessary for growth, development, and reproduction.
- Scientists are studying the plant genome to better understand how genes interact and affect plant traits.
- Genome sequencing has enabled researchers to identify specific genes responsible for traits such as disease resistance and yield potential.

- Plant genetics is a complex field that involves studying the genetic makeup of plants to enhance their growth and productivity.
- Genetics plays a crucial role in determining the traits and characteristics of different plant species.
- Researchers are constantly exploring new techniques and technologies to advance the field of plant genetics.
Plant Biotechnology

- Plant biotechnology has revolutionized agriculture by creating genetically modified crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases.
- Researchers in plant biotechnology are working on developing new methods to increase crop yields and improve food security worldwide.
- The field of plant biotechnology holds great potential for addressing environmental challenges such as climate change and soil degradation.

- Genetic engineering has revolutionized the agricultural industry by allowing scientists to create plants with enhanced traits.
- Many farmers are embracing genetic engineering to help produce crops that are more resilient to pests and diseases.
- The controversy surrounding genetic engineering in plant biotechnology continues to spark debates among policymakers and environmentalists.

- Transgenic plants are often created to be resistant to pests or herbicides.
- Some transgenic plants have been engineered to produce higher yields or have better nutritional value.
- There is ongoing debate over the safety and environmental impact of transgenic plants.

- Biotechnology has revolutionized the agricultural industry, allowing for the development of more resilient and productive crops.
- Plant biotechnology has the potential to address global food security issues by creating plants that are more resistant to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses.
- Many companies are investing heavily in biotechnology research to discover new ways to enhance crop yields and nutritional content.

- GMOs have been a controversial subject in the food industry due to concerns about their potential impact on human health and the environment.
- Many countries have strict regulations in place regarding the cultivation and sale of GMOs.
- Some argue that GMOs are necessary to address global food security issues and increase crop yields.

- Scientists are using gene editing techniques to develop crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases.
- Gene editing has the potential to revolutionize agriculture by creating crops that are more nutritious and drought-resistant.
- The ethical implications of gene editing in plants are still being debated, as some argue that it could lead to unforeseen consequences in the environment.

- Plant tissue culture is commonly used in the production of disease-free plants for commercial use.
- Researchers are using plant tissue culture to study the effects of various hormones on plant growth and development.
- Plant tissue culture has revolutionized the way plants are propagated and studied in agriculture and horticulture.

- Plant transformation is a key technique used in biotechnology to enhance crop yield and resistance to pests.
- Researchers are constantly improving plant transformation methods to make them more efficient and precise.
- The success of plant transformation has revolutionized agriculture by creating genetically modified crops with desirable traits.
Quick Facts
- Botany is the scientific study of plants, including their structure, growth, reproduction, metabolism, development, diseases, and interactions with other organisms.
- The first recorded botanist was Theophrastus, a student of Aristotle, who wrote “Enquiry into Plants” and “On the Causes of Plants” in the 4th century BC.
- There are over 400,000 known species of plants, ranging from tiny mosses to towering trees, and new species are still being discovered and classified by botanists around the world.
- Plants play a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth by producing oxygen through photosynthesis, providing food for humans and animals, and serving as habitats for countless organisms in ecosystems.
- Botanists often specialize in different subfields such as plant taxonomy, plant physiology, plant ecology, and ethnobotany, which focuses on the cultural significance of plants to human societies.
